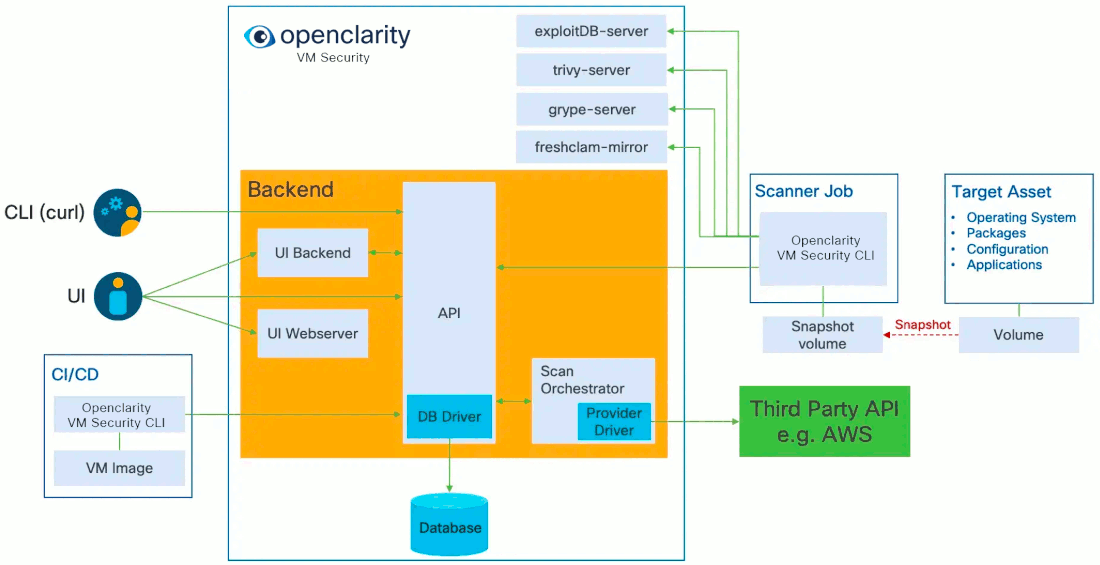
1 - OpenClarity Stack
Today, OpenClarity has two halves, the OpenClarity control plane, and the OpenClarity CLI.
The OpenClarity control plane includes several microservices:
-
API Server: The OpenClarity API for managing all objects in the OpenClarity system. This is the only component in the system which talks to the DB.
-
Orchestrator: Orchestrates and manages the life cycle of OpenClarity scan configs, scans and asset scans. Within the Orchestrator there is a pluggable “provider” which connects the orchestrator to the environment to be scanned and abstracts asset discovery, VM snapshotting as well as creation of the scanner VMs. (Note The only supported provider today is AWS, other hyperscalers are on the roadmap)
-
UI Backend: A separate backend API which offloads some processing from the browser to the infrastructure to process and filter data closer to the source.
-
UI Webserver: A server serving the UI static files.
-
DB: Stores the OpenClarity objects from the API. Supported options are SQLite and Postgres.
-
Scanner Helper services: These services provide support to the OpenClarity CLI to offload work that would need to be done in every scanner, for example downloading the latest vulnerability or malware signatures from the various DB sources. The components included today are:
- grype-server: A rest API wrapper around the grype vulnerability scanner
- trivy-server: Trivy vulnerability scanner server
- exploitDB server: A test API which wraps the Exploit DB CVE to exploit mapping logic
- freshclam-mirror: A mirror of the ClamAV malware signatures
The OpenClarity CLI contains all the logic for performing a scan, from mounting attached volumes and all the pluggable infrastructure for all the families, to exporting the results to OpenClarity API.
These components are containerized and can be deployed in a number of different ways. For example our cloudformation installer deploys OpenClarity on a VM using docker in an dedicated AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC).
Once the OpenClarity server instance has been deployed, and the scan configurations have been created, OpenClarity will discover VM resources within the scan range defined by the scan configuration (e.g., by region, instance tag, and security group). Once the asset list has been created, snapshots of the assets are taken, and a new scanner VM are launched using the snapshots as attached volumes. The OpenClarity CLI running within the scanner VM will perform the configured analysis on the mounted snapshot, and report the results to the OpenClarity API. These results are then processed by the OpenClarity backend into findings.
2 -
Initiate scan using the cli
Reporting results into file
./bin/openclarity-cli scan --config ~/testConf.yaml -o outputfile
If we want to report results to the OpenClarity backend, we need to create asset and asset scan object before scan because it requires asset-scan-id
Reporting results to OpenClarity backend
ASSET_ID=$(./bin/openclarity-cli asset-create --file assets/dir-asset.json --server http://localhost:8080/api) --jsonpath {.id}
ASSET_SCAN_ID=$(./bin/openclarity-cli asset-scan-create --asset-id $ASSET_ID --server http://localhost:8080/api) --jsonpath {.id}
./bin/openclarity-cli scan --config ~/testConf.yaml --server http://localhost:8080/api --asset-scan-id $ASSET_SCAN_ID
Using one-liner:
./bin/openclarity-cli asset-create --file docs/assets/dir-asset.json --server http://localhost:8080/api --update-if-exists --jsonpath {.id} | xargs -I{} ./bin/openclarity-cli asset-scan-create --asset-id {} --server http://localhost:8080/api --jsonpath {.id} | xargs -I{} ./bin/openclarity-cli scan --config ~/testConf.yaml --server http://localhost:8080/api --asset-scan-id {}
2.1 - Example CLI Configuration
This section provides a sample configuration for scanner families supported by the OpenClarity CLI tool. Each family can be enabled or disabled, and configured with specific options. The configuration is used to define which scanners to run, what inputs to scan, and the configuration for each scanner.
# This file contains a sample configuration for scanner families supported by the OpenClarity CLI tool.
# Each family can be enabled or disabled, and configured with specific options.
# The configuration is used to define the scanners to run, the inputs to scan, and the configuration for each scanner.
# SBOM (Software Bill of Materials) scanner family
sbom:
enabled: false # Enable or disable SBOM scanner family
analyzers_list: # List of analyzers to run
- "syft"
- "trivy"
- "windows"
- "gomod"
inputs: # List of inputs to scan
- input: "node:slim"
input_type: "image" # Type of input (image, rootfs, etc.)
# - input: "/mnt"
# input_type: "rootfs"
# - input: "nginx:1.10"
# input_type: "image"
# merge_with: # Merge multiple SBOMs into one
# - sbom_path: "nginx.11.cdx.json" # Path to SBOM file to merge with
local_image_scan: true # Scan images from local docker daemon (true) or from remote registry (false)
registry:
skip-verify-tls: false # Skip TLS verification
use-http: false # Use HTTP instead of HTTPS
auths: # Registry authentication
authority: "authority"
username: "username"
password: "password"
token: "token"
output_format: "cyclonedx-json" # Output format for SBOMs (cyclonedx-json, cyclonedx-xml, spdx-json, spdx-tv, syft-json)
analyzers_config: # Configuration for each analyzer
syft:
scope: "Squashed" # Scope of the scan (squashed, all-layers)
exclude_paths: # Paths to exclude from the scan
- "./dev"
- "./proc"
## Overrides parent sbom configs
# local_image_scan: ...
# registry: ...
trivy:
timeout: 300 # Timeout in seconds
cache_dir: /tmp/.trivy/cache # Cache directory
temp_dir: /tmp/.trivy/ # Temp directory
## Overrides parent sbom configs
# local_image_scan: ...
# registry: ...
# Vulnerabilities scanner family
vulnerabilities:
enabled: false # Enable or disable vulnerabilities scanner family
scanners_list: # List of scanners to run
- "grype"
- "trivy"
inputs: # List of inputs to scan
- input: "nginx:1.12"
input_type: "image" # Type of input (image, rootfs, etc.)
# - input: "nginx:1.13"
# input_type: "image"
- input: "/mnt/"
input_type: "sbom"
local_image_scan: true # Scan images from local docker daemon (true) or from remote registry (false)
registry: # Registry configuration
skip-verify-tls: false
use-http: false
auths:
authority: "authority"
username: "username"
password: "password"
token: "token"
scanners_config: # Configuration for each scanner
grype:
mode: "LOCAL" # Mode of operation (LOCAL, REMOTE). LOCAL uses local database, REMOTE uses Grype server.
local_grype_config:
update_db: true # Update the database
db_root_dir: "/tmp/" # Database root directory
listing_url: "https://toolbox-data.anchore.io/grype/databases/listing.json" # Listing URL
max_allowed_built_age: "120h" # Max allowed built age
listing_file_timeout: "60s" # Listing file timeout
update_timeout: "60s" # Update timeout
scope: "squashed" # Scope of the scan (squashed, all-layers)
## Overrides parent sbom configs
# local_image_scan: ...
# registry: ...
remote_grype_config:
grype_server_address: "" # Grype server address
grype_server_timeout: "2m" # Grype server timeout
grype_server_schemes: [] # Grype server schemes
trivy:
timeout: 300 # Timeout in seconds
cache_dir: /tmp/.trivy/cache # Cache directory
temp_dir: /tmp/.trivy/ # Temp directory
server_addr: "trivy.example.com" # Trivy server address
server_token: "token" # Trivy server token
## Overrides parent sbom configs
# registry: ...
# Secrets scanner family
secrets:
enabled: false # Enable or disable secrets scanner family
scanners_list: # List of scanners to run
- "gitleaks"
strip_input_paths: false # Strip input paths from the output
inputs: # List of inputs to scan
- input: "/"
input_type: "rootfs"
scanners_config: # Configuration for each scanner
gitleaks:
binary_path: "/usr/local/bin/gitleaks" # Path to gitleaks binary
# Exploits scanner family
exploits:
enabled: false # Enable or disable exploits scanner family
scanners_list: # List of scanners to run
- "exploitdb"
inputs: # List of inputs to scan
- input: "CVE-2024-5535,CVE-2023-3446"
input_type: "csv"
scanners_config: # Configuration for each scanner
exploit_db:
base_url: "http://localhost:1326" # Base URL for the ExploitDB server
# Misconfigurations scanner family
misconfiguration:
enabled: false # Enable or disable misconfigurations scanner family
scanners_list: # List of scanners to run
- "cisdocker"
- "lynis"
- "fake"
strip_input_paths: false # Strip input paths from the output
inputs: # List of inputs to scan
- input: "/"
input_type: "rootfs"
scanners_config: # Configuration for each scanner
cisdocker:
timeout: "60s" # Timeout
registry: # Registry configuration
skip-verify-tls: false
use-http: false
auths:
authority: "authority"
username: "username"
password: "password"
token: "token"
lynis:
binary_path: "/usr/local/bin/lynis" # Path to Lynis binary
# InfoFinder scanner family
infofinder:
enabled: false # Enable or disable infofinder scanner family
scanners_list: # List of scanners to run
- "sshTopology"
strip_input_paths: false # Strip input paths from the output
inputs: # List of inputs to scan
- input: "/"
input_type: "rootfs"
scanners_config: {}
# Malware scanner family
malware:
enabled: false # Enable or disable malware scanner family
scanners_list: # List of scanners to run
- "clam"
- "yara"
strip_input_paths: false # Strip input paths from the output
inputs: # List of inputs to scan
- input: "/"
input_type: "rootfs"
scanners_config: # Configuration for each scanner
clam:
freshclam_binary_path: "/usr/local/bin/freshclam" # Path to freshclam binary
freshclam_config_path: "/etc/clamav/freshclam.conf" # Path to freshclam configuration file
alternative_freshclam_mirror_url: "" # Alternative freshclam mirror URL. Config option cannot include servers under *.clamav.net.
use_native_clamscan: false # Scan using native clamscan command (true) instead of daemon clamdscan (false)
clamscan_binary_path: "/usr/local/bin/clamscan" # Path to clamscan binary
clamscan_exclude_files: # Files to exclude from the scan
- "^.*\\.log$"
clamscan_exclude_dirs: # Directories to exclude from the scan
- "^/sys"
clam_daemon_binary_path: "/usr/local/bin/clamd" # Path to clamd binary
clam_daemon_config_path: "/etc/clamav/clamd.conf" # Path to clamd configuration file
clam_daemon_client_binary_path: "/usr/local/bin/clamdscan" # Path to clamdscan binary
yara:
yara_binary_path: "/usr/local/bin/yara" # Path to yara binary
compiled_rule_url: "" # URL to download compiled rules
rule_sources: # List of rule sources
- name: ""
url: ""
yarac_binary_path: "/usr/local/bin/yarac" # Path to yarac binary
cache_dir: "/tmp/.yara" # Cache directory
directories_to_scan: [] # Directories to scan
# Rootkits scanner family
rootkits:
enabled: false # Enable or disable rootkits scanner family
scanners_list: # List of scanners to run
- "chkrootkit"
strip_input_paths: false # Strip input paths from the output
inputs: # List of inputs to scan
- input: "/"
input_type: "rootfs"
scanners_config: # Configuration for each scanner
chkrootkit:
binary_path: "/usr/local/bin/chkrootkit" # Path to chkrootkit binary
# Plugins scanner family
plugins:
enabled: false # Enable or disable plugins scanner family
binary_mode: false # Use binary mode for plugins
binary_artifacts_path: "" # Path to binary artifacts
binary_artifacts_clean: true # Clean binary artifacts after execution
scanners_list: # List of scanners to run
- "kics"
inputs: # List of inputs to scan
- input: "/"
input_type: "rootfs"
scanners_config: # Configuration for each scanner
kics:
image_name: "ghcr.io/openclarity/openclarity-plugin-kics:latest" # Image name for KICS plugin
config: "{\"preview-lines\": 3, \"report-formats\": [\"json\" ], \"platform\": [], \"max-file-size-flag\": 100, \"disable-secrets\": true, \"query-exec-timeout\": 60, \"silent\": true, \"minimal\": true}" # Configuration example for KICS
3 - OpenClarity SDKs
See the scanner module for the SDK.